
Sony is enhancing accessibility for deaf gamers with a newly patented in-game sign language translator. This innovative technology facilitates real-time translation between different sign languages within video games.
Sony Patents ASL to JSL Translator for Video Games
Leveraging VR and Cloud Gaming Technologies
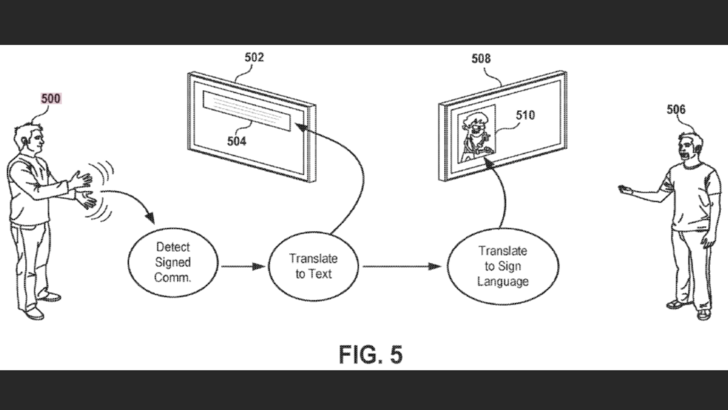
Sony's patent, titled "TRANSLATION OF SIGN LANGUAGE IN A VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT," details a system enabling real-time translation, for example, from American Sign Language (ASL) to Japanese Sign Language (JSL). This aims to bridge communication gaps for deaf players during in-game interactions. On-screen avatars will visually represent translated sign language in real-time. The process involves a three-step translation: sign gestures are first converted to text, then translated to the target language, and finally rendered as the corresponding sign language gestures.
As Sony explains in the patent: "Implementations of the present disclosure relate to methods and systems for capturing sign language of one user (e.g., Japanese), and translating the sign language to another user (e.g., English). Because sign languages vary depending on geographical origins, sign language is not universal. This provides a need for appropriately capturing the sign language of one user, understanding the native language, and generating new sign language as output for another user in their native sign language."
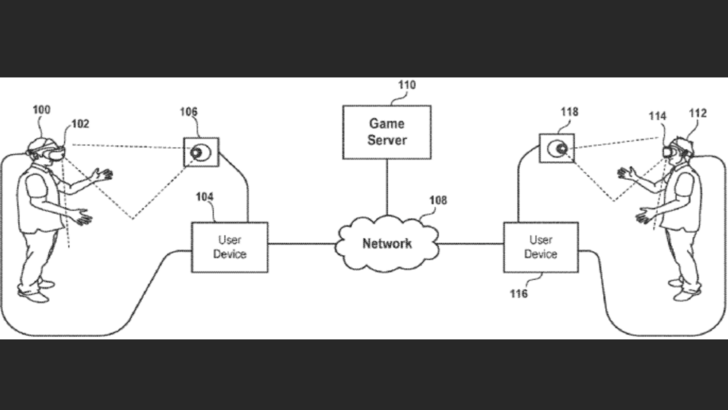
Sony envisions implementing this system using VR headsets (HMDs) connected to PCs, game consoles, or other computing devices. The patent describes how the HMD would provide immersive gameplay, with the user device rendering graphics for display.
Furthermore, Sony proposes seamless communication between user devices and a game server over a network. This game server manages the game's state, synchronizing the virtual environment across connected devices. The patent also suggests integration with cloud gaming systems, where the server renders and streams video, enabling shared gameplay experiences. This setup allows users to interact within the same virtual environment over a shared network or server.






